


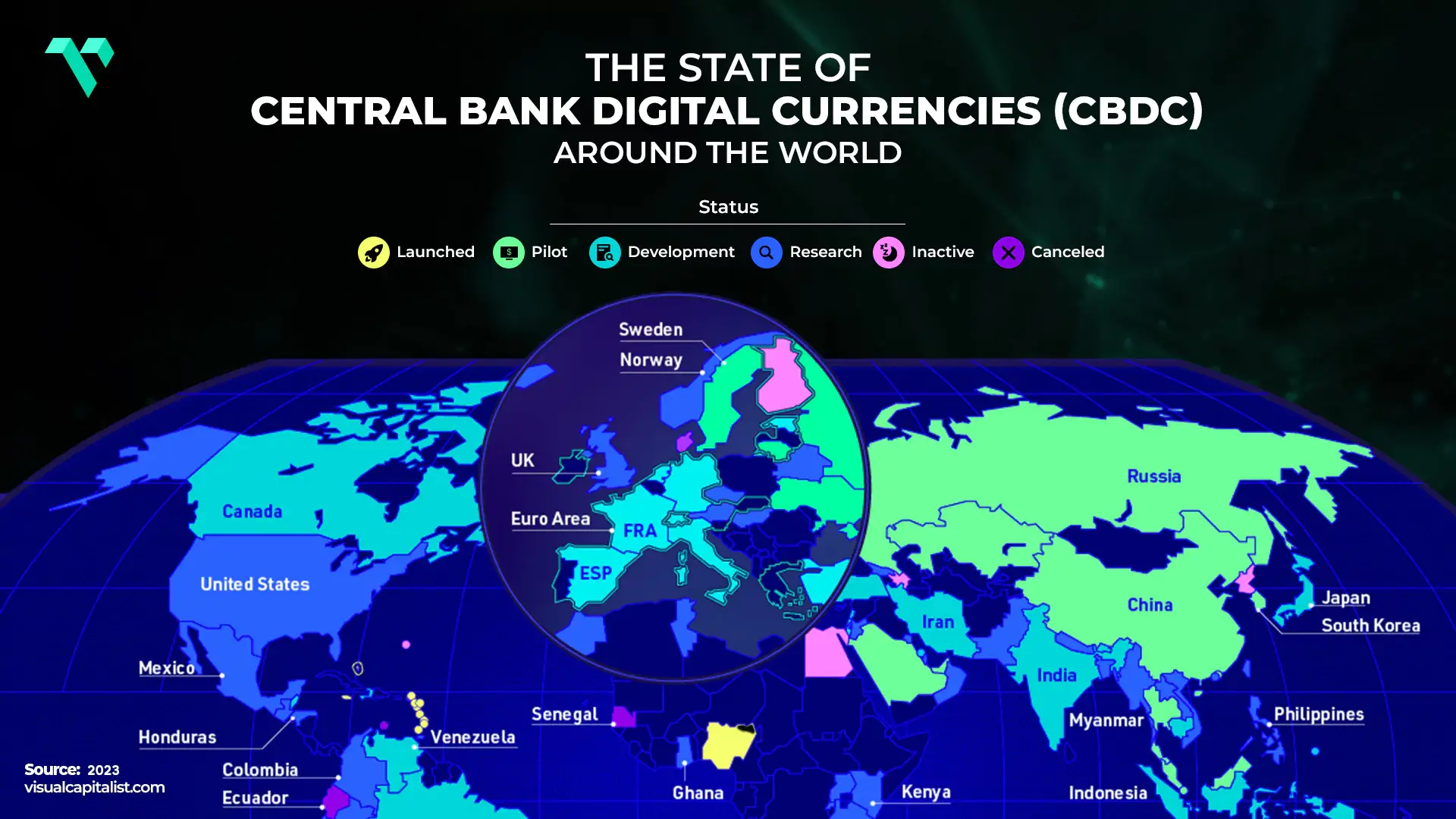
With the digital age completely transforming our lives, the financial sector is no biggie. CBDC are emerging as a pivotal innovation to redefine the future of money. In early 2023, a shocking prediction emerged, forecasting a whopping 260,000 percent surge in the transaction value facilitated by central bank digital currencies (CBDC) from 2023 to 2030. That being said, more than 100 countries, representing over 95% of global GDP, actively explore CBDCs while some nations brainstorm pre-launch strategies and full-scale implementations. Some notable examples include Nigeria, Jamaica, the Bahamas’ Sand Dollar, China’s Digital Yuan, and the European Union’s Digital Euro.
It is predicted that the CBDC project is a long-term trend. For instance, the European CBDC, the Digital Euro, will launch between 2026 and 2029. The United States Federal Reserve curated its first review in 2022, which means it follows countries that are developing a retail-focused CBDC. Countries like the UK and Canada are researching blockchain technology to optimize banking procedures rather than being customer-focused.
CBDCs mean “Central Bank Digital Currencies” They are a digital form of a nation's fiat currency regulated and issued by the central bank. What’s interesting about CBDCs is that unlike stablecoins and other cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin, which operate on a decentralized blockchain, CBDC operate on centralized money issued directly by central banks. They are designed as digital counterparts to traditional fiat currencies. This provides the benefits of digital transactions while maintaining trust and stability associated with central bank-issued money.
There are generally three types of CBDCs that are developed and implemented.
It is designed for use in interbank settlements and transactions by financial organizations such as banks and payment processors. Wholesale CBDCs can improve efficiency in the financial system and reduce the risk of settlement failures.
Retail CBDC is similar to traditional cash in that it may be used to make immediate payments or purchases. This type of CBDC is mainly for the general public. Digital wallets controlled by the central bank or authorized intermediaries can be used to access retail CBDCs.
This type of CBDC collects the attributes of both retail and Wholesale CBDCs. It can be used for interbank settlements parallel to consumer transactions. Hybrid CBDCs create an efficient and integrated financial process.

It is important to compare CBDCs with other cryptocurrencies to understand their exceptional potential. Let's take Bitcoin, for instance.
Bitcoin operates on a decentralized blockchain, as the transactions are verified by a network of nodes without a central authority. This decentralization requires enhanced security and privacy measures. Moreover, it also poses concerns regarding price stability and regulatory oversight.
On the contrary, CBDCs are centralized digital currencies issued by central banks, which allows greater control over the currency supply and stability. While Bitcoin works independently of conventional financial systems, CBDCs are designed to integrate effortlessly into existing economic systems, offering a digital complement to physical currency.
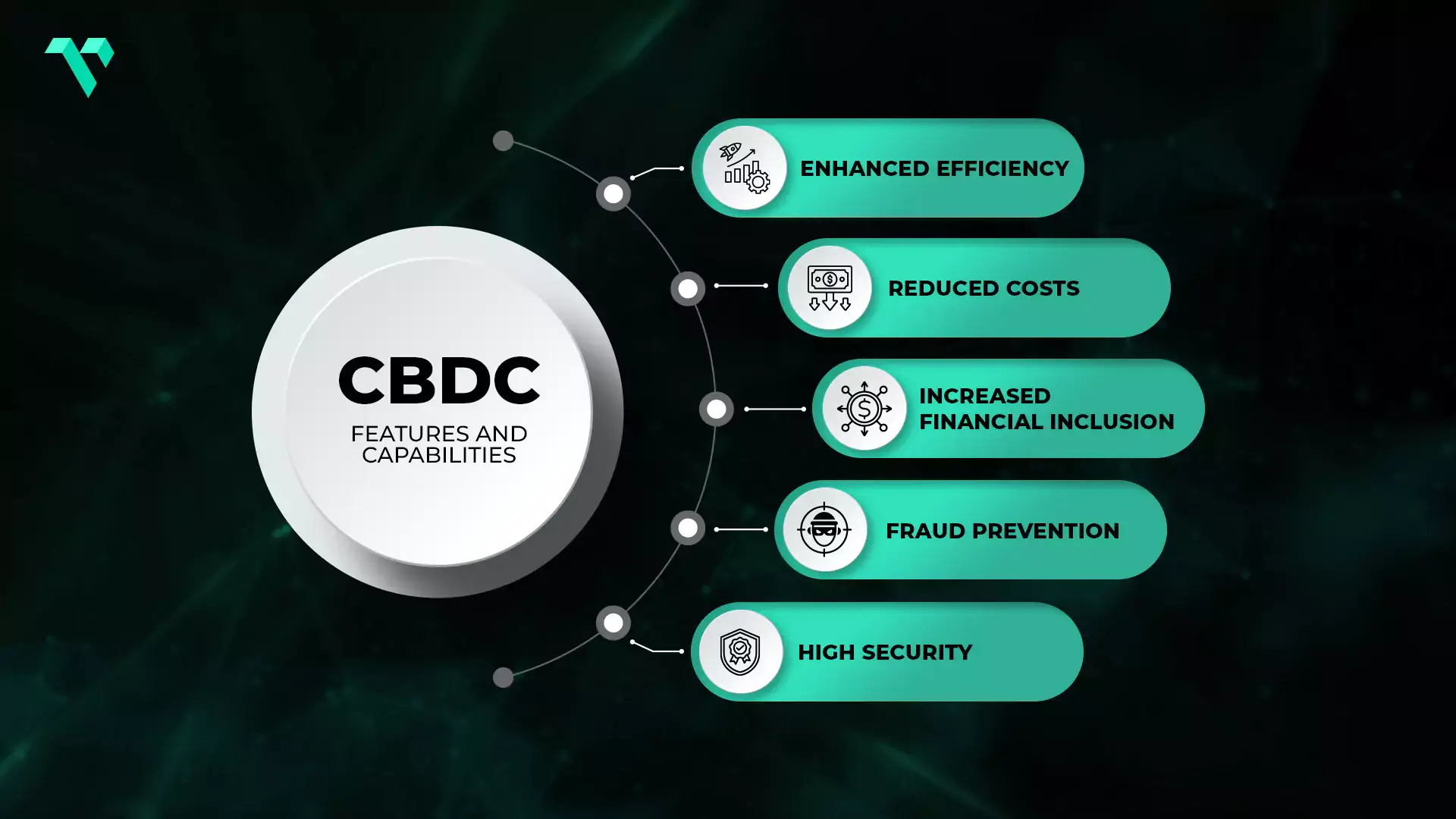
Financial inclusion is one of the most significant benefits of CBDCs. Around the world, access to banking services is quite limited. CBDCs provide a direct financial interaction, allowing individuals to participate in the digital economy without a bank account. A good example is the Bahamas’ Sand Dollar, which aims to improve financial inclusion in a nation with a dispersed population.
CBDCs provide streamlined payment systems. This reduces the need for intermediaries and lowers the cost of transactions. CBDCs can also expedite cross-border transactions, unlike current banking systems, which are often slow and costly. A prime example of this can be the European Central Bank’s Digital Euro, which makes effortless digital payments across the Eurozone, minimizing transaction fees and reducing reliance on cash.
Digital currencies offer enhanced security features such as traceability and verification, which assist in reducing fraud and money laundering. Blockchain technology, which brings many CBDC projects under its umbrella, provides a transparent, fraud-proof ledger, ensuring the integrity of transactions. This can increase trust in the financial infrastructure and lower the risks of illicit activities and counterfeiting.
China’s digital currency, the Digital Yuan, also known as “e-CNY,” is seen at the forefront of CBDC development. To enhance the digital economy and reduce reliance on cash, the People’s Bank of China has been conducting extensive trials in major cities. The Digital Yuan is China’s broader strategy to modernize its financial infrastructure and enhance control over monetary policy.
The European Central Bank is exploring the Digital Euro to make digital payments seamless and accessible across Europe. The Digital Euro aims to complement cash by offering a secure and effective means of payment for everyone, including all businesses and citizens. The ECB has stressed the importance of user privacy and financial stability in its design considerations.
Did you know? The Bahamas was among the first countries to launch CBDC with its Sand Dollar. To improve financial inclusion, the Sand Dollar offers a digital payment solution for the island's residents. This mainly benefits people living in remote areas who have limited access to traditional banking services. The massive success of the Sand Dollar has given valuable insights to other nations considering similar interests.
With the remarkable potential to redefine how we use and interact with money, the rise of CBDCs has marked a significant shift in the financial world. As more countries consider developing and implementing CBDCs, we can foresee changes in payment systems, banking practices, and even the global economy.
For CBDCs to be successful, they must collaborate and integrate with the existing financial systems. This involves central banks, commercial banks, and technology experts joining to ensure smooth implementation and user adoption. Interoperability between different CBDCs will be crucial for international transactions and global financial stability. Implementing these digital currencies can be critical in curating adequate global and economic stability.
The beginning of CBDCs can ignite innovation and competition in the financial world. Traditional banks and fintech companies will need to adapt to the changing horizon. This will lead to the development of effective financial systems, new financial services, and products. This competition can drive improvements in security, customer experience, and efficiency.
CBDCs represent significant innovation with the potential to reshape the course of financial grounds and the future of money. By swapping physical cash with a digital alternative, CBDCs can offer several benefits, such as increased financial inclusion, enhanced efficiency, and improved security. Thus, the evolution of CBDCs is vast and promising to revolutionize the way we make transactions globally. If you wish to stay ahead of the curve, platforms such as Vanarchain offer innovative solutions in blockchain technology, providing the infrastructure needed to support the implementation of CBDCs.